Researchers at Boston Children's Hospital and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health have discovered a new mechanism of immunity that suggests that there may be a better way to protect vulnerable children and adults against Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal) infection, which leads to serious illnesses, including pneumonia and meningitis (inflammation of the brain).
Breadcrumb
- Home
- Conditions & Treatments
- Pneumonia
What is pneumonia?
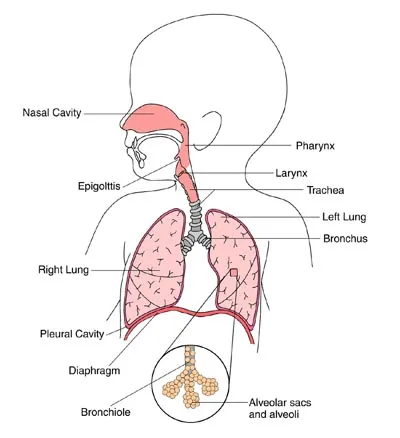
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or chemical irritants. It is a serious infection in which air sacs in the lungs fill with pus and other liquid.
- Pneumonia may be lobar (affects one or more sections — lobes — of the lungs) or bronchial (affects patches throughout both lungs, also called “bronchopneumonia”).
- Pneumonia is most common in winter and spring.
- About 10 to 15 percent of children with a respiratory infection have pneumonia.
What are the types of pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is caused by various bacteria, most often the bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other bacteria that may cause bacterial pneumonia are:
- Group B streptococcus (most common in newborns)
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Group A streptococcus (most common in children over age 5)
Bacterial pneumonia may have a quick onset and you may notice the following symptoms in your child:
- Fever
- Productive cough (your child coughs up mucus)
- Pain in the chest
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Decrease in appetite
- Fatigue
Viral pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses, including:
- Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, most often seen in children under age 5
- Parainfluenza virus
- Influenza virus (flu)
- Adenovirus
Early symptoms of viral pneumonia are the same as those of bacterial pneumonia. However, with viral pneumonia, the respiratory involvement happens slowly. You may notice your child wheezing, and his cough may worsen.
Viral pneumonias may make your child susceptible to bacterial pneumonia.
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by an atypical bacteria. They generally cause a mild pneumonia involving both lungs that affects all age groups. Mycoplasma pneumonia is sometimes called “walking pneumonia."
Symptoms of this kind of pneumonia are different from the other types. The symptoms usually do not begin with a cold, and may include:
- Fever and cough are the first to develop
- Persistent cough that may last three to four weeks
- Severe cough that may produce some mucus
Other less common pneumonias may be caused by the inhaling of food, liquid, gases, or dust, or by fungi.
Symptoms & Causes
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
All pneumonias share the following symptoms. Keep in mind that each child may experience them differently:
- Fever
- Chest or stomach pain
- Decrease in appetite
- Chills
- Breathing fast or hard
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Not feeling well
- Fussiness
Diagnosis & Treatments
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually made based on the season and the extent of your child’s illness. Your child’s physician may diagnose simply on a thorough history and physical examination, but may also include any of following tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Chest X-ray: A diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
- Blood tests: Blood count for evidence of infection; arterial blood gas to analyze the amount of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood.
- Sputum culture: A diagnostic test performed on the material that is coughed up from the lungs and into the mouth. A sputum culture is often performed to determine if an infection is present.
- Pulse oximetry: An oximeter is a small machine that measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. To obtain this measurement, a small sensor (like a Band-Aid) is taped onto your child’s finger or toe. When the machine is on, a small red light can be seen in the sensor. The sensor is painless and the red light does not get hot.
How is pneumonia treated?
Treatment may include antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia. Antibiotics may also speed recovery from mycoplasma pneumonia and some special cases. There is no clearly effective treatment for viral pneumonia, which usually clears up on its own. Other treatment may include:
- Appropriate diet
- Increased fluid intake (giving your child more liquids to drink)
- Cool mist humidifier in your child's room
- Acetaminophen (for fever and discomfort)
- Medication for cough
Your child may be treated in the hospital if she is having severe breathing problems. While in the hospital, treatment may include:
- Intravenous (IV) or oral antibiotics
- Intravenous (IV) fluids, if your child is unable to drink well
- Oxygen therapy
- Frequent suctioning of your child's nose and mouth (to help get rid of thick secretions)
- Breathing treatments, as ordered by your child's physician





