Myopia | Symptoms & Causes
What are the symptoms of myopia?
Myopia is usually noted in children around the ages of 9 or 10. It might be discovered if your child cannot read the blackboard from the back of the room, but can see to write and read without a problem.
Other signs and symptoms may include:
- headaches
- nausea after reading
- holding books close to his face
- writing with his head very close to the table
- sitting very close to the television
- squinting when looking at things that are far away
What causes refractive errors?
Refractive errors (myopia and hyperopia, or "farsightedness") have been found to cluster in families. These inherited patterns may be:
- dominant (one gene was inherited from a parent with a refractive error)
- recessive (caused by two genes, one inherited from each parent, who may or may not have a refractive error)
- multifactorial (combination of genes and environment)
Refractive errors are also present in a number of genetic disorders, such as Marfan syndrome and Down syndrome.
Myopia | Diagnosis & Treatments
What treatments are available for myopia?
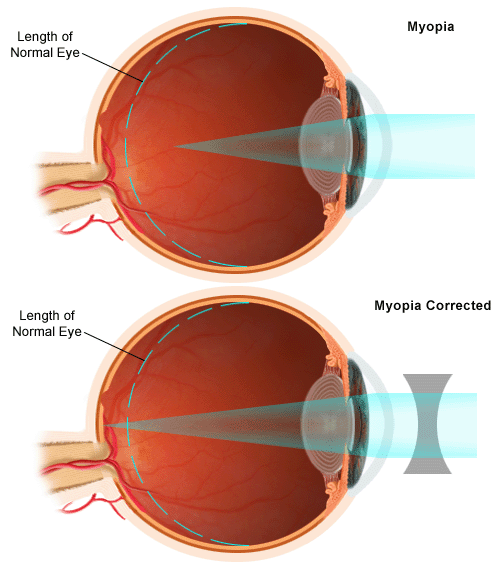
Eyeglasses or contact lenses may help to correct or improve myopia by helping the eye focus light.
How Boston Children's approaches myopia
The Low Vision Service at Boston Children's Hospital is one of the few services of its kind in New England devoted exclusively to meeting the unique needs of children with a wide range of visual disorders. The service is aimed at determining what visual aids can help your child best utilize his remaining vision to its fullest potential — whether we are helping him to participate in school, read, write, see the blackboard, or learn to drive.
The Contact Lens Service at Boston Children's Hospital provides complete contact lens care for infants and children. The program offers fitting of contact lenses and follow-up care for therapeutic and cosmetic needs.